Evaluation of the safe consumption of aqueous extract of flour from Stichopus variegates
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15419/bmrat.v6i11.574Keywords:
Safe consumption, Stichopus variegatus flour, Water extractAbstract
Introduction: Sea cucumbers of phylum Echinodermata and class Holothuroidea are found on the seafloor worldwide and are widely used in Asian folk medicine. Objective: In this article, our team provide information of the safety consumption as a reference material for the development of functional foods derived from sea cucumber flour.
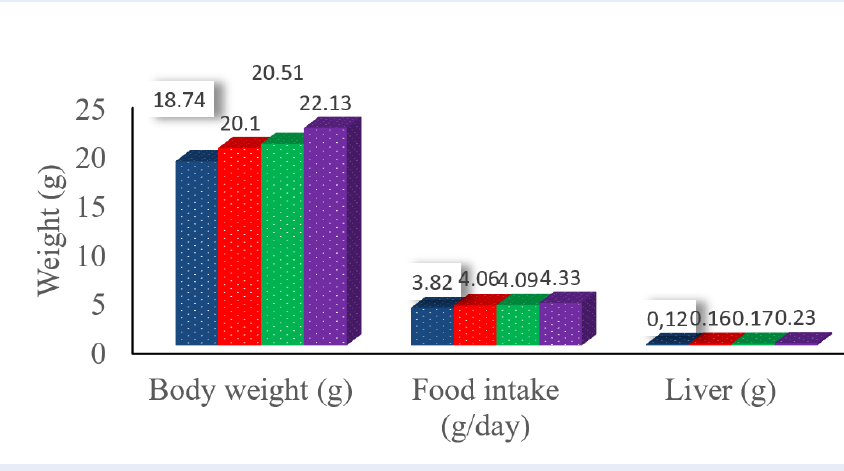
Methods: Stichopus variegatus caught in South Lampung, Indonesia, was processed into flour by vacuum oven, then extracted using hot water to produce Stichopus variegatus-water extract (SV-WE). In the end treatment, the kidney and liver of male BALB/c mice was analysed using hematoxylin and eosin for a histology data, and blood serum was analysed for biochemical parameters.
Results: There was no clinical symptoms in serum biochemistry, histology, and mortality after daily oral administration of SV-WE to male BALB/c mice at 1000, 1500, or 2500 mg/kg body weight/day for 4 weeks.
Conclusion: The consumption of SV-WE to male BALB/c mice was safe, its LD50 has higher than 2500 mg/kg/day. Stichopus variegatus sea cucumber flour could be utilized as an ingredient in functional foods.
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright The Author(s) 2017. This article is published with open access by BioMedPress. This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC-BY 4.0) which permits any use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author(s) and the source are credited.
