Exploring the Effect of Phytochemical Extract (Benincasa sp.) on the Inflammatory Mediators and Regulatory Pathways of Acute Cisplatin Nephrotoxicity in Pre-clinical Mouse Model
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15419/bmrat.v11i6.896Keywords:
Mechanism of acute kidney injury, Cisplatin, Benincasa cerifera, Immunological Markers, Nephrotoxicity, Inflammatory CytokinesAbstract
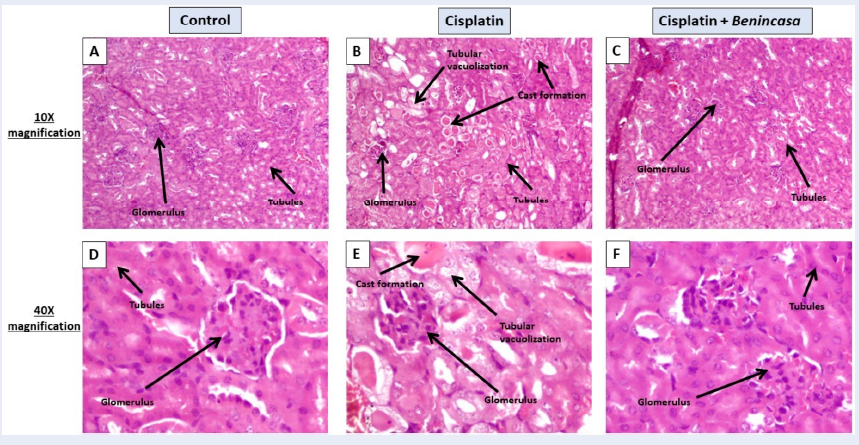
Introduction: Cisplatin-induced acute nephrotoxicity is typically manifested by a decrease in kidney function, electrolyte imbalances, and acute kidney injury (AKI). Most therapies for AKI are costly and have serious side effects. Utilizing phytotherapy for the prevention of kidney disease has the potential to reduce both treatment expenses and the occurrence of associated side effects. Benincasa cerifera (BC) offers extensive advantages owing to its anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and anti-diabetic characteristics. This study aims to demonstrate the protective effects of BC on the inflammatory mediators and regulatory pathways in a cisplatin-induced acute kidney injury (AKI) model.
Methods: Fifteen 6–8-week-old female BALB/c mice (weighing 20-25 g) were divided into three groups as follows: (I) Control, (II) Cisplatin, (III) Cisplatin + BC. The disease was induced with a single dose (15 mg/kg) of cisplatin on day 0, followed by treatment with an ethanolic extract of BC (500 mg/kg). On day 7, the sacrificed mice were used to study the histopathological, biochemical, immunological, and inflammatory parameters.
Results: Treatment with BC successfully restored the clonogenic potential of the kidney, blood, spleen, and bone marrow cells. Flow cytometry showed that cisplatin-induced abnormalities in cellular circulation and the migration of CD45+B220+ B cells, CD4+, CD8+ T lymphocytes, and F4/80+ cells in the blood were significantly recovered with the treatment of BC. This study also found that BC inhibited the upregulation of different inflammatory cytokines, which were involved in the Th1, Th2, and Th17 response.
Conclusion: Phytochemical-based novel treatment strategies developed from this work will provide safe options for patients and assist in reducing the disease burden of AKI.
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright The Author(s) 2017. This article is published with open access by BioMedPress. This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC-BY 4.0) which permits any use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author(s) and the source are credited.
