The effects of monocusp valve implantation and transannular patch angioplasty on pulmonary regurgitation and right ventricular failure after total correction of tetralogy of fallot
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15419/bmrat.v7i5.607Keywords:
Tetralogy of Fallot, Pulmonary Regurgitation, Transannular Patch, Congenital Heart Disease, Right Ventricular Failure, Monocusp ReconstructionAbstract
Background: Pulmonary regurgitation (PR) is often known as an acquired condition after surgical correction of tetralogy of Fallot (TOF). Therefore, the present study aimed to compare the use of monocusp valve (MV) implantation and transannular patch (TAP) angioplasty on PR and right ventricular (RV) failure following surgery to repair TOF.
Methods: This prospective randomized clinical trial (RCT) was performed on a total number of 60 patients undergoing reconstructive surgery on TOF. For this purpose, TAPs without and with monocusp reconstruction were used in Group I (n = 30 patients) and Group II (n = 30 patients), respectively. Then, echocardiographic parameters, mortality rates, and clinical data from pediatric intensive care unit (PICU) were evaluated during a follow-up period for both groups.
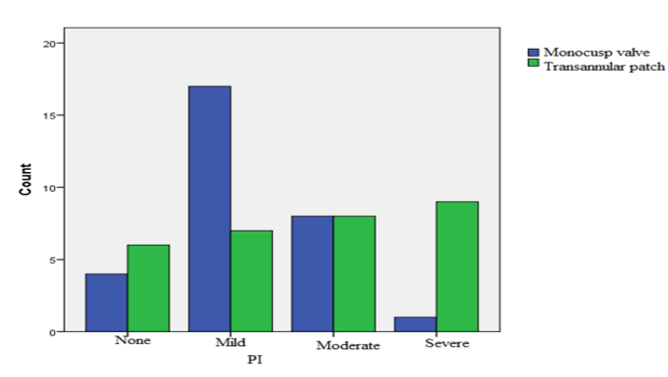
Results: Out of the 60 patients undergoing surgery and evaluated, 39 individuals were male (65%) and the rest were female (n = 21 patients, 35%). No significant difference was observed in terms of age, body weight, body surface area (BSA), mortality rate, and ejection fraction (EF) between the two study groups. The findings revealed that the number of patients with severe PR was higher in the group receiving TAP angioplasty. Furthermore, the difference between the two groups with regards to severity of PR was significant (p = 0.012).
Conclusion: It was concluded that MV reconstruction of TOF is effective in reducing pulmonary artery (PA) and pulmonary valve (PV) insufficiency.
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright The Author(s) 2017. This article is published with open access by BioMedPress. This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC-BY 4.0) which permits any use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author(s) and the source are credited.
