Characterization of synovium-derived mesenchymal stem cells from joints with osteochondritis dissecans
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15419/bmrat.v7i10.645Keywords:
Synovial-derived MSCs, Potency, Differentiation, Osteochondritis dissecansAbstract
Introduction: Osteochondritis dissecans (OCD) is a pathologic condition that occurs in children as well as adults. OCD is often managed based on the extent of ischemia and the stage of the disease. Synovial tissue collected during an arthroscopic procedure might serve as an ideal source for autologous mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) with a potential for regenerative medicine of cartilage. Therefore, the present in vitro study aimed to evaluate the potency characteristics of synovium-derived MSCs (SMSCs) from joints with OCD for prospective autologous therapy.
Methods: Primary culture of SMSCs was established and basic cellular properties, such as morphology, growth kinetics and clonal propagation ability, were analyzed. The expression of phenotypic markers, including CD29, CD44, CD90, CD34 and CD45, was assessed by flow cytometry and immunocytochemistry. Mesodermal differentiation into osteocytes, chondrocytes and adipocytes was performed using standard protocols. Expression of chondrocyte-specific markers was analyzed by reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR).
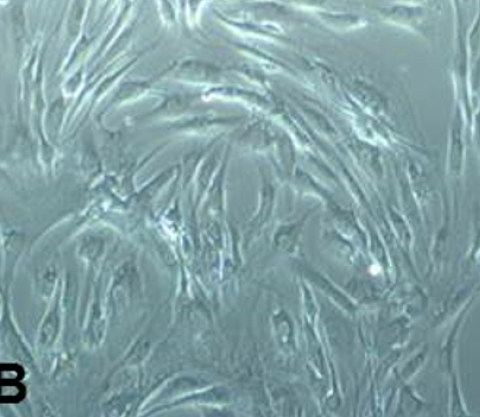
Results: Isolated SMSCs displayed fibroblast-like morphology with > 95% cell viability and had high proliferative rates with a shorter doubling time. The cells showed positive expression of CD29, CD44 and CD90, but were negative for CD34 and CD45 markers. Upon induction, SMSCs were successfully differentiated into osteogenic, chondrogenic and adipogenic lineages. Chondrogenesis was more prominent in SMSCs than osteogenesis. Chondrogenesis was further confirmed by the expression of aggrecan and collagen type IIα1 markers.
Conclusion: SMSCs showed greater proliferation and an enhanced ability for chondrogenic differentiation. Synovium can be harvested with minimal tissue damage and donor-site morbidity and might serve as an alternative autologous source of MSCs for cartilage-tissue regeneration.
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright The Author(s) 2017. This article is published with open access by BioMedPress. This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC-BY 4.0) which permits any use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author(s) and the source are credited.
