The role of tumor-derived exosomes in tumor immune escape: A concise review
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15419/bmrat.v7i11.650Keywords:
Cancer, Exosomes, Tumor immune escapeAbstract
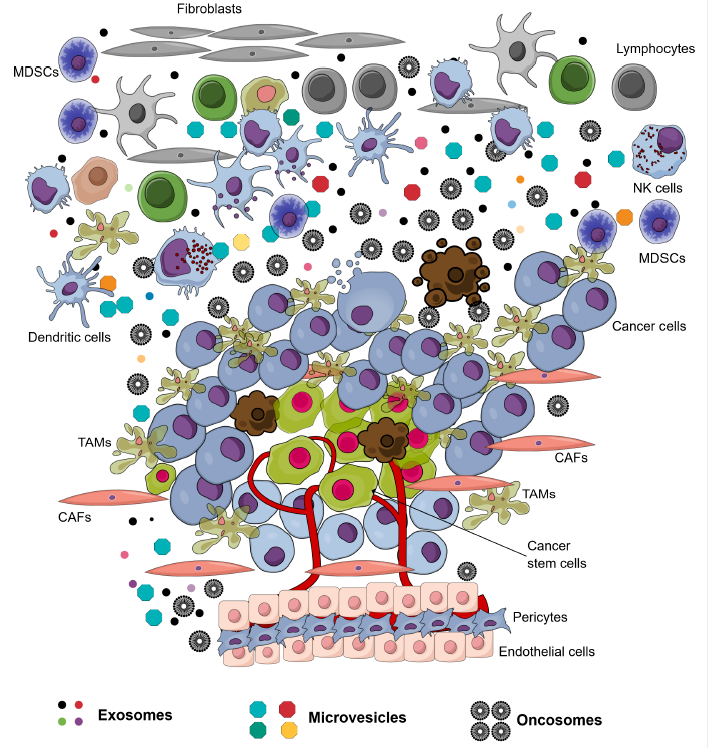
Exosomes are small vesicles secreted by viable cells into the microenvironment. These vesicles bring various compositions, including lipids, RNAs and proteins, which carry information from producer cells to target cells. Cancer cells also produce exosomes, termed as tumor-derived exosomes (TDEs), which play important roles in immune modulation, angiogenesis and metastasis of tumors. This review summarizes the roles of TDEs in tumor immune escape mechanisms. TDEs affect all kinds of tumor-associated immune cells, including natural killer (NK) cells, dendritic cells (DCs), T and B lymphocytes, and myeloid-derived suppressor cells (MDSCs). Generally, TDEs suppress the immune system to promote tumor immune escape, thereby significantly contributing to tumorigenesis and metastasis.
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright The Author(s) 2017. This article is published with open access by BioMedPress. This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC-BY 4.0) which permits any use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author(s) and the source are credited.
