A retrospective analysis of pyogenic liver abscess and antibiotic resistivity of common pathogens in Peshawar
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15419/bmrat.v7i12.656Keywords:
Pyogenic liver abscess (PLA), E.coli, K pneumonia, Citrobacter, Antibiotic resistanceAbstract
Background: Pyogenic liver abscess (PLA) is a rare but life-threatening disease, with a frequency ranging from 10.83 to 17.45 per 100,000 persons. The major cause of PLA is bacterial infection of liver parenchyma. The present research study was designed to investigate the common microbes causing PLA in Peshawar (Pakistan) and to evaluate a variety of the most capable and efficient antibiotics for treatment of PLA.
Methods: A 7-year (2012 - 2018) retrospective demographic study of medical records of all PLA patients (n = 379) admitted to the Hayatabad Medical Complex (HMC) and Khyber Teaching Hospital (KTH) was initially performed. The demographic study was followed by biochemical tests and antibiotic resistivity tests of microorganisms, isolated from available samples and selected from literature using web services.
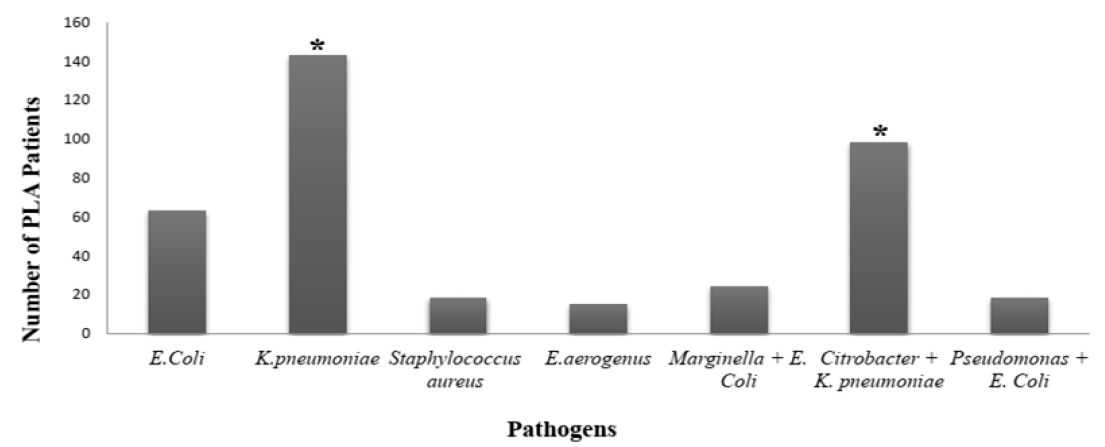
Results & Conclusion: The demographic data revealed that 70% of the PLA patients were under the age of 50, with male predominance (male to female ratio of 3:1). It was concluded that K. pneumonia, poly-microbes (K. pneumonia and Citrobacter), and E. coli are the most common microbes involved in causing PLA in the population of Peshawar. E.coli, Citrobacter and K. pneumonia were sensitive to Cefixime and Ciprofloxacin (100% sensitivity rate), but showed significant resistance against Amoxycillin, Oxacillin and Fusidic Acid. It is, therefore, prudent to practice susceptibility-directed antibiotic therapy.
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright The Author(s) 2017. This article is published with open access by BioMedPress. This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC-BY 4.0) which permits any use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author(s) and the source are credited.
