Fenugreek-mediated synthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles and evaluation of its in vitro and in vivo antitumor potency
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15419/bmrat.v8i8.687Keywords:
Cell cycle, Ehrlich ascites carcinoma, Fenugreek seeds extract, Zinc oxide nanoparticlesAbstract
Introduction: Zinc oxide nanoparticles (ZnONPs) are one of the most interesting metal oxide nanoparticles due to their easy functionalization, biocompatibility, and anticancer impact. The current study was designated to evaluate the in vitro and in vivo anticancer potency of biologically synthesized ZnONPs.
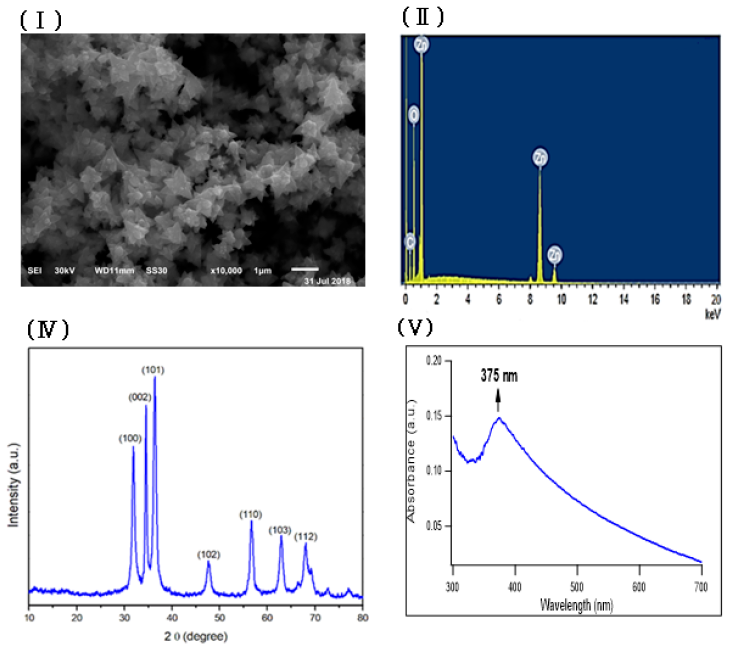
Methods: Fenugreek seeds’ extract was used to prepare ZnONPs, and then characterized by scanning electron microscope (SEM), energy dispersive X-ray (EDX), X-ray diffraction (XRD), UV-V spectroscopy and transmission electron microscope (TEM). The in vitro antitumor activity of biogenic ZnONPs against different cancer cells was evaluated by MTT assay. In addition, their anticancer activities alone or in combination with Doxorubicin were investigated against EAC model using intraperitoneal injection day after day.
Results: Biologically synthesized ZnONPs showed a cytotoxic potency against different cancer cell lines combined with lower toxicity against normal cells. Further, the in vivo study revealed that the treatment by ZnONPs alone or combined with doxorubicin hampered the proliferation of EAC in mice by lowering the ascetic volume and the number of viable tumor cells. Moreover, ZnONPs alone or combined with doxorubicin induced the cell cycle arrest at G0/G1 phase and apoptosis by up-regulating the expression of caspase-3 and Bax and down-regulating the expression of Bcl-2 proteins.
Conclusion: Our study indicated that the biogenic ZnONPs could be instructive to future cancer treatment research.
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright The Author(s) 2017. This article is published with open access by BioMedPress. This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC-BY 4.0) which permits any use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author(s) and the source are credited.
