Remarkable and Prolonged Response to Melphalan and High-Dose Dexamethasone Combined Therapy of a Patient with Light-Chain Cardiac Amyloidosis
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15419/bmrat.v10i11.846Keywords:
cardiac amyloidosis, melphalan, high-dose dexamethasone, treatmentAbstract
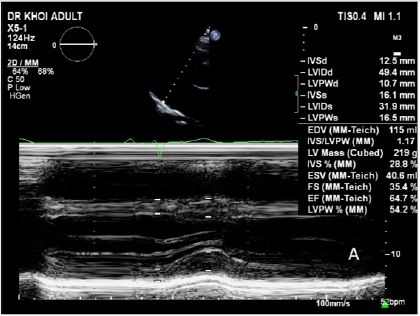
This case report highlights the successful management of a patient with light chain amyloidosis and New York Heart Association (NYHA) functional class IV heart failure who was ineligible for an autologous stem cell transplant (ASCT). They were managed with an oral melphalan and dexamethasone regimen in addition to standard heart failure treatment according to European Society of Cardiology-American Heart Association guidelines. They responded well to treatment, showing symptom improvement and the ability to function at the NYHA class II level. They were closely monitored throughout treatment, with regular testing for infective screening, systemic biochemical workup, echocardiography, and monitoring of N-terminal pro-B-type natriuretic peptide (NTproBNP) and troponin T levels. After 24 cycles of high-dose oral melphalan and dexamethasone chemotherapy, the patient could discontinue treatment and continue follow-up monitoring. The most recent workup showed significantly improved cardiac function, with decreased left ventricular wall thickness, improved diastolic function and strain, and decreased NT-proBNP level. This case report demonstrates the importance of considering alternative treatment options for patients ineligible for ASCT due to advanced heart involvement. It also highlights the potential benefits of an oral melphalan and dexamethasone regimen combined with standard heart failure treatment in improving clinical outcomes in these patients.
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright The Author(s) 2017. This article is published with open access by BioMedPress. This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC-BY 4.0) which permits any use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author(s) and the source are credited.
