Ameliorative Effect of Quercetin against Modification Induced by 5-Fluorouracil on Alpha-2-Macroglobulin
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15419/bmrat.v8i12.711Keywords:
5-Fluorouracil, alpha-2-macroglobulin, circular dichorism, flavonoids, FTIR, quercetin, reactive oxygen speciesAbstract
Introduction: Alpha-2-macroglobulin (α2M) is large glycoprotein, found in the plasma of vertebrates and invertebrates, which plays a major role in regulation and transport. In this study, we report the interaction of 5-fluorouracil (5-FU) with α2M and the protective effect of quercetin against 5-FU induced modification of α2M.
Methods: Various biochemical and biophysical methods and techniques were employed to determine the binding interaction between α2M-5-FU and the preventive effect of quercetin on 5-FU induced modification of α2M. Fluorescence microscopy was performed to analyze the formation of free radicals by 5-FU and to examine the scavenging effect of quercetin.
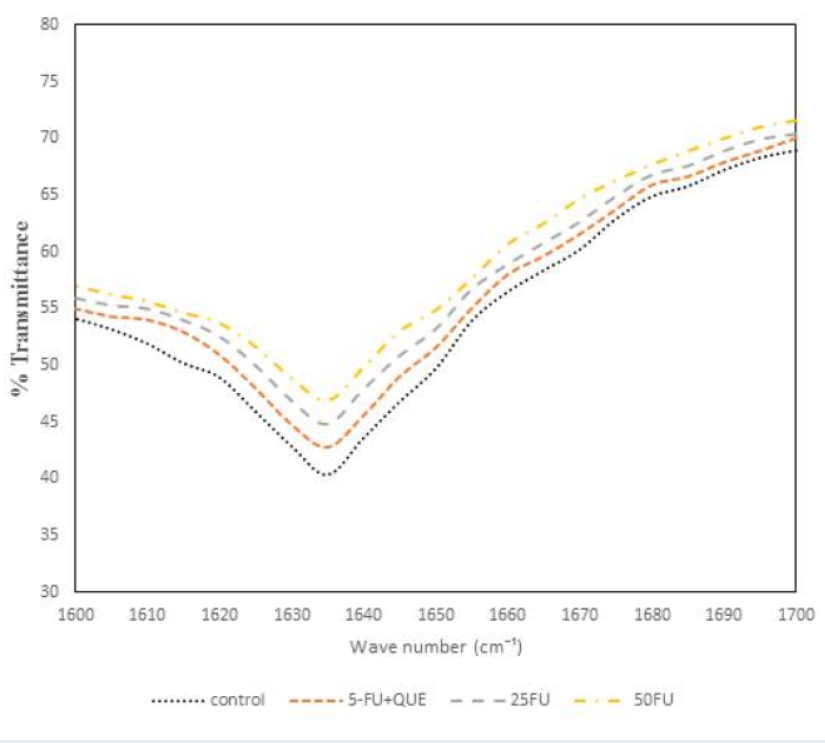
Results: Our results of antiproteinase activity assay show that the 5-FU-α2M interaction causes functional inactivation of sheep α2M, while the 5-FU-α2M complex after exposure to quercetin regains its native conformation. Intrinsic fluorescence results suggest an increase of 5-FU quenching in the fluorescence intensity, and when the mixture was incubated with quercetin the α2M-FU-quercetin mixture showed the same intensity as that of native protein. The absorption spectra of 5-FU-α2M complex suggest the formation of a complex leading to increase in absorbance. CD and FTIR spectroscopy show 5-FU causes secondary structural alteration of α2M and quercetin provides a protective role against structural modification.
Conclusion: Our study suggests that 5-FU produces reactive oxygen species (ROS) in the presence of light and compromises the integrity of α2M. Quercetin quenches the ROS formed by 5-FU and helps the protein to maintain its native conformation. We have demonstrated the protective effect of quercetin for the first time against the toxicity induced by 5-FU on α2M.
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright The Author(s) 2017. This article is published with open access by BioMedPress. This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC-BY 4.0) which permits any use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author(s) and the source are credited.
