Elevated expression of SKP2 correlates with poor prognosis in osteosarcoma: a bioinformatics analysis
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15419/bmrat.v8i12.714Keywords:
Biomarkers, Cell cycle, Gene expression, GEO database, Osteosarcoma, SKP2Abstract
Introduction: Osteosarcoma (OS) is the most prevalent kind of bone cancer, but the tumorigenesis and underlying molecular drivers of OS remain unknown. The instability of the cell cycle regulation system, which leads to uncontrolled cell proliferation, is a typical characteristic of carcinogenesis. This study aimed to investigate the expression of SKP2 in human OS and assessed its prognostic value in OS patients.
Methods: Three gene expression profile datasets GSE28424, GSE42352 and GSE21257 were obtained from the GEO database. The Wilcoxon rank-sum test was performed to evaluate the differential expression of the SKP2 gene between the OS and the control groups in the GSE28424 and GSE42352 datasets, and the correlation between SKP2 expression and Huvos grade was analysed in the GSE21257 dataset. Subsequently, PPI network, GO and KEGG analyses were constructed. Furthermore, survival analysis between high SKP2 expression group and low SKP2 expression group was performed using the Kaplan–Meier method and log-rank test. In addition, the UALCAN database was used to investigate the association between SKP2 expression and sarcoma.
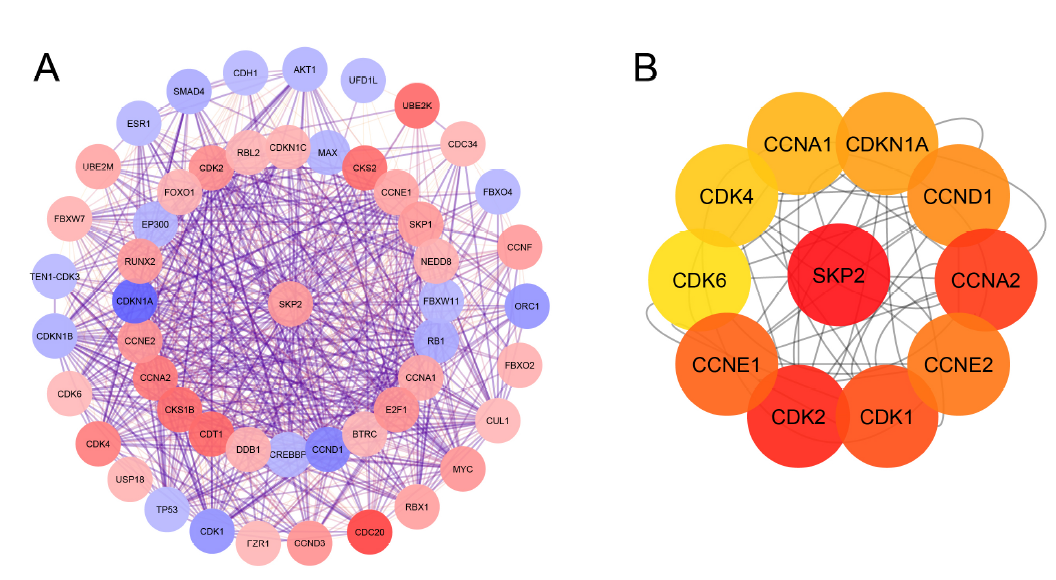
Results: The expression level of SKP2 in OS cells was significantly higher than that in normal bones and mesenchymal stem cell samples. Furthermore, the level of SKP2 expression was observed to decrease as Huvos grade increased. The PPI network was established, and the top ten SKP2-related genes were identified, including CDKs (1, 2, 4, and 6), Cyclin A1-2, E1-2, D1, and CDKN1A. The survival analysis showed that the elevated SKP2 expression level was significantly related to the overall survival of OS patients.
Conclusion: Our work adds to our knowledge of SKP2's function in OS and suggests that it might be used as a therapeutic target in the future.
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright The Author(s) 2017. This article is published with open access by BioMedPress. This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC-BY 4.0) which permits any use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author(s) and the source are credited.
