Association between anti-collagen type II autoantibodies and the acute rheumatoid arthritis phenotype in a cohort of rheumatoid arthritis patients
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15419/bmrat.v9i4.736Keywords:
Rheumatoid Arthritis, Anticollagen type II antibodies, Disease Activity Score, Acute rheumatoid arthritis phenotypeAbstract
Background: This study aims to evaluate serum concentrations of anti-collagen type II (anti-CII) antibodies in Iraqi patients with a severe rheumatoid arthritis (RA) phenotype and investigate the relationship between higher concentrations of anti-CII antibodies and higher levels of inflammation.
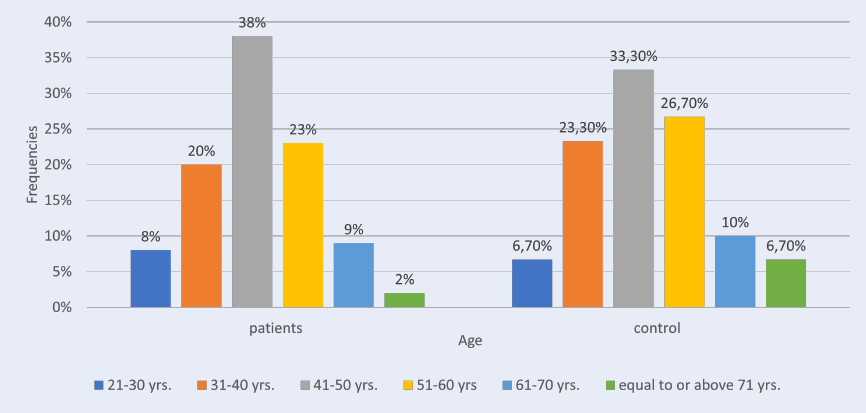
Methods: This study was conducted with 100 patients with RA who were admitted to the Arthritis Consulting Clinic, Baghdad Teaching Hospital, Iraq. The patients selected were patients diagnosed with RA about 2 to 3 years ago. Data on the patients were collected, including the results of tests for anti-CII concentrations, and were compared with data from 30 healthy subjects. Healthcare workers aspirated 5 ml of blood from each control and patient subject, divided into two parts. The workers transferred the first one (3 ml) into a plain tube, allowed 30 minutes for it to clot, and then isolated the serum by centrifugation at 2500 rpm for 10 minutes for measurement of the anti-collagen type II antibodies by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). The workers transferred the second part (2 ml) to the tube containing EDTA for hematological measurement of the erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR).
Results: This study found that the levels of anti-collagen type II antibodies were significantly higher in patients with RA than in healthy controls (p-value > 0.05). The study found a statistically significant positive moderate correlation with ESR (r = 0.56, p-value = 0.000) and a statistically significant positive strong correlation between disease activity score-28 (DAS28) and anti-collagen type II antibodies (r = 0.65, p-value = 0.000) in RA patients.
Conclusions: Anti-CII antibodies can be considered an important parameter for the early detection of RA and can be used to determine the activity of RA.
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright The Author(s) 2017. This article is published with open access by BioMedPress. This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC-BY 4.0) which permits any use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author(s) and the source are credited.
