Morin: a promising nutraceutical therapy for modulation of the NF-κB/NOX-2/IL-6/HO-1 signaling pathways in paracetamol-induced liver toxicity
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15419/bmrat.v9i9.763Keywords:
IL-6, liver, morin, NF-kB, NOX-2, paracetamol, TNF-a, toxicityAbstract
Introduction: Paracetamol overdose potentially causes liver injury. This study aimed to evaluate the impact of morin against paracetamol overdose-induced hepatotoxicity.
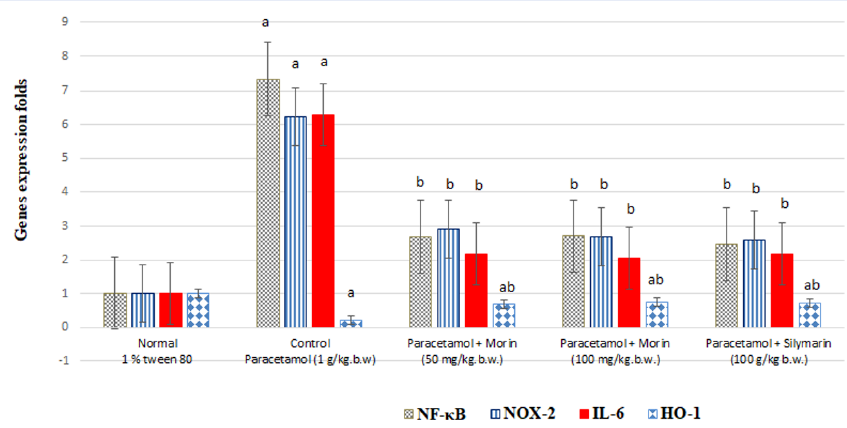
Methods: Thirty albino rats weighing 185 ± 5 g were randomly selected from five groups: group I: orally administered with 1% Tween 80; group II: administered with 1 g paracetamol; group III: administered with 1 g paracetamol and 50 mg morin; group IV: administered with 100 mg paracetamol and morin; and group V: administered with 100 mg paracetamol and silymarin, with all treatments administered for 14 days.
Results: Morin and silymarin significantly protected the rats against induced alterations in the plasma total cholesterol, triacylglycerol, and HDL-C levels as well as the liver ALT, AST, ALP, LDH, protein thiol, GSH, SOD, CAT, MDA, and tumor necrosis factor-alpha levels. Furthermore, morin significantly inhibited the expression of NF-κB, NADPH oxidase-2, and interleukin-6 and induction of heme oxygenase-1 compared with paracetamol. The histological results indicated that morin protected the liver tissues against the toxic effect of paracetamol.
Conclusion: Morin significantly depletes the side effects of paracetamol and protects the liver tissue from the resulting free radicals.
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright The Author(s) 2017. This article is published with open access by BioMedPress. This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC-BY 4.0) which permits any use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author(s) and the source are credited.
