Application of a Finite Mixture Model to Assess the Role of CD4+ T Cell Count as a Predictor of Memory Loss in HIV+ Patients
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15419/bmrat.v10i4.803Keywords:
HIV, CD4 lymphocytes, Memory, AIDS, Finite mixture modelsAbstract
Introduction: Memory impairment is one of the most important complications in patients with HIV infection. The syndrome is caused by reductions in brain volume and the count of circulating CD4+ lymphocytes. This study was conducted to evaluate the relationship between CD4+ lymphocyte count and memory function in HIV+ patients.
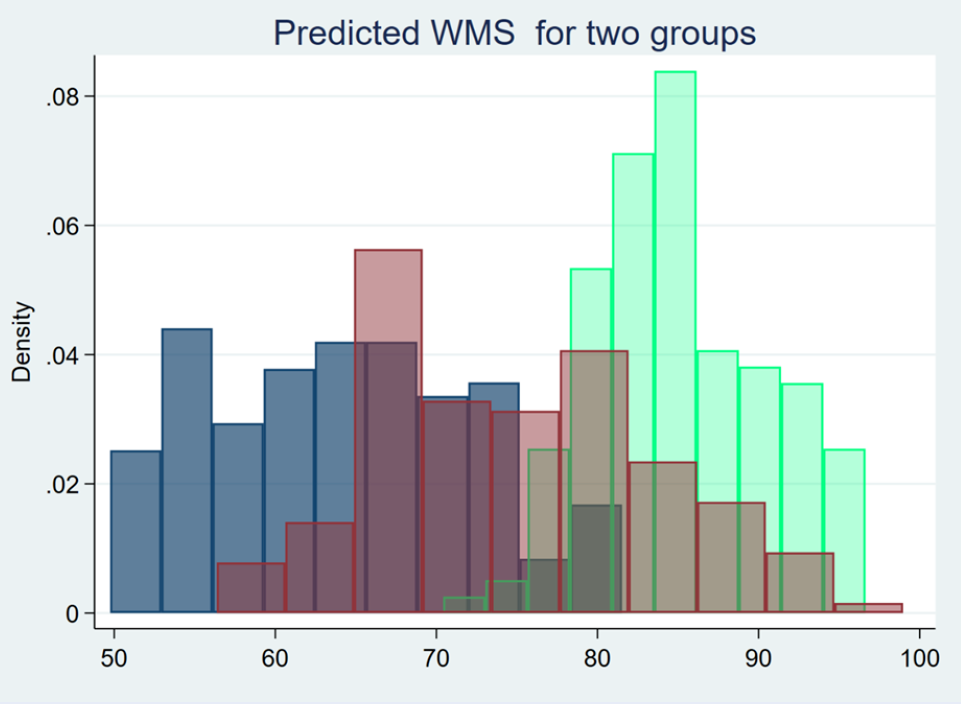
Methods: This descriptive-analytical study was conducted on 150 HIV+ patients referred to the Behavioral Disorders Counseling Center of Kermanshah City. Memory function in patients was measured using the Wechsler memory scale. The patients' CD4+ cell counts and demographic information were extracted from their medical files. The data were recorded in STATA version 16 software and analyzed using regression and finite mixture models.
Results: The meansstandard deviations of memory function in three classes of patients were 63.99 +/- 7.02, 75.01 +/- 14.72, and 85.14 +/- 6.43. The results showed that a decrease in CD4+ cell count increased the risk of memory loss in patients (P < 0.001). In addition, higher age (P < 0.001), female gender (P < 0.001), and a lower education level (P < 0.001) were significantly associated with an increased risk of memory loss in HIV+ patients.
Conclusion: The results of the present study confirmed the findings of previous studies noting memory impairment in HIV+ patients as a result of immune system suppression, including the depletion of CD4+ cells. Therefore, it is necessary to monitor cognitive function in these patients and to implement measures to strengthen their memory performance.
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright The Author(s) 2017. This article is published with open access by BioMedPress. This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC-BY 4.0) which permits any use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author(s) and the source are credited.
