The cytotoxic effect of Vernonia amygdalina Del. extract on myeloid leukemia cells
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15419/bmrat.v10i8.827Keywords:
apoptosis, BCR-ABL, leukaemia, transcriptional expression, V. amygdalina Del.Abstract
Introduction: This study aimed to demonstrate the cytotoxic effect of a bitter leaf (Vernonia amygdalina Del.) ethanol extract on myeloid leukemia cells.
Methods: The plant extract was prepared using the maceration method. The toxicity assays used the trypan blue exclusion method. Flow cytometry and reverse transcription PCR methods were used to deduce the mechanism of action.
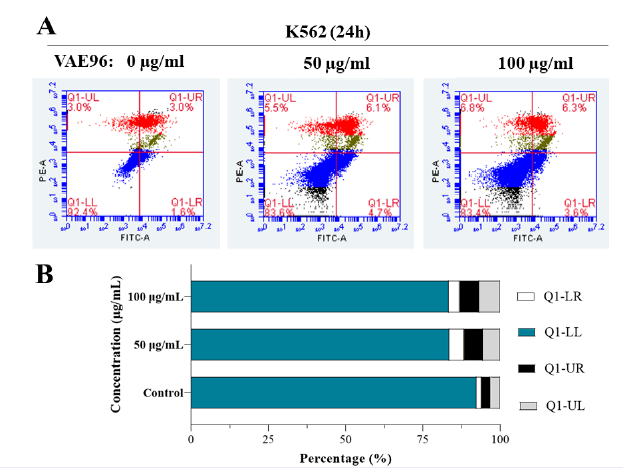
Results: The V. amygdalina Del. extract strongly affected K562 cells, with a half-maximal inhibitory concentration of 8.78 ? 2.224 ?g/mL. The extract could induce apoptosis and arrest the cell cycle in K562 cells. The extract increased the mRNA levels of caspase 3 (CASP3), baculoviral IAP repeat containing 5 (BIRC5/survivin), and phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K) and decreased the mRNA levels of retinoblastoma transcriptional corepressor 1 (RB1/pRB), B cell lymphoma/leukemic 2 (BCL2), BCL2-like 1 (BCL2L1/BCL-XL), caspase 9 (CASP9), and the breakpoint cluster region (BCR)-Abelson (ABL) fusion gene.
Conclusion: The V. amygdalina Del. extract strongly inhibited the acute myeloid leukemia cell line K562. It was found to arrest the cell cycle and induce apoptosis by regulating the expression of related genes that predicted targeting BCR-ABL downregulation.
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright The Author(s) 2017. This article is published with open access by BioMedPress. This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC-BY 4.0) which permits any use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author(s) and the source are credited.
