Detection of COVID-19 Patients through SARS-CoV-2 Antigen Assay using Chemiluminescence Immunoassay: Comparison to RT-PCR Method
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15419/bmrat.v11i4.879Keywords:
COVID-19, SARS-CoV-2 antigen assay, Chemiluminescence Immunoassay (CLEIA), RT-PCR, Diagnostic methodAbstract
Background: Accurate and reliable diagnostic tools are essential in effectively managing infectious diseases during the ongoing global COVID-19 pandemic. For this study, the RT-PCR assay was used as the reference method, and the objective was to determine the concordance rate, sensitivity, and specificity of the SARS-CoV-2 antigen assay (SARS-CoV-2 Ag) using the chemiluminescence immunoassay (CLEIA) technique for identifying COVID-19 patients.
Method: A total of 231 nasopharyngeal swab samples were collected from individuals with either COVID-19 (cycle threshold (Ct) values ≤ 40) or non-COVID-19 (Ct values > 40 or undetected) diagnoses. These samples were examined using the SARS-CoV-2 Ag.
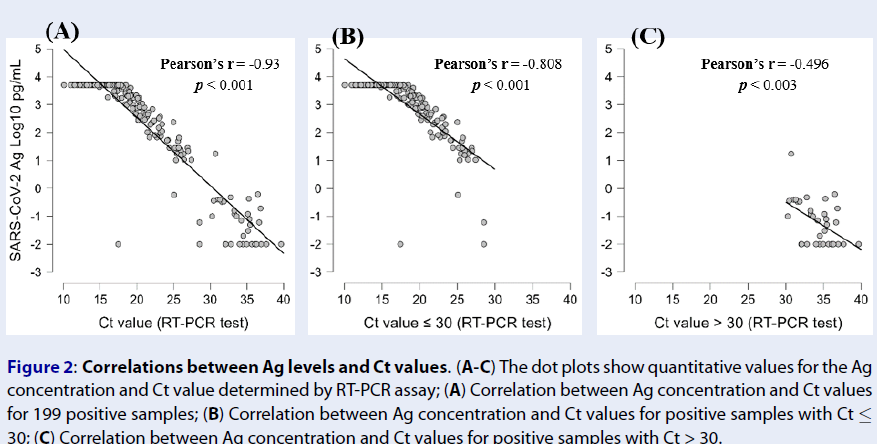
Results: The overall concordance rate of the SARS-CoV-2 Ag was 84.0% (194/231), with a sensitivity of 81.4% (162/199) and 100% specificity (32/32). When samples were categorized into two Ct value groups, the SARS-CoV-2 Ag demonstrated a sensitivity of 97.6% for samples with a Ct value ≤ 30 and 2.9% for samples with a Ct value > 30. Moreover, the antigen concentration determined by the SARS-CoV-2 Ag showed a strong inverse correlation with the Ct value obtained from the RT-PCR assay (r = -0.93, p < 0.001).
Conclusion: The SARS-CoV-2 Ag proves to be a potentially effective tool for diagnosing and monitoring COVID-19 patients, particularly in settings where the RT-PCR assay is not available.
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright The Author(s) 2017. This article is published with open access by BioMedPress. This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC-BY 4.0) which permits any use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author(s) and the source are credited.
