The effects of the Panax Vietnamensis ethanol fraction on proliferation and differentiation of mouse neural stem cells
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15419/bmrat.v6i10.571Keywords:
Ethanol fraction, Mouse neural stem cells, NSCs, Panax vietnamensis, Stem cell proliferationAbstract
Introduction: Panax vietnamensis Ha et Grushv. (Ngoc Linh ginseng) – a new species recently discovered in Vietnam – has received much interest due to its rich content of saponins, including those unknown. This study assessed the effects of the Ngoc Linh ginseng extract fractions on proliferation and differentiation of cultured mouse neural stem cells.
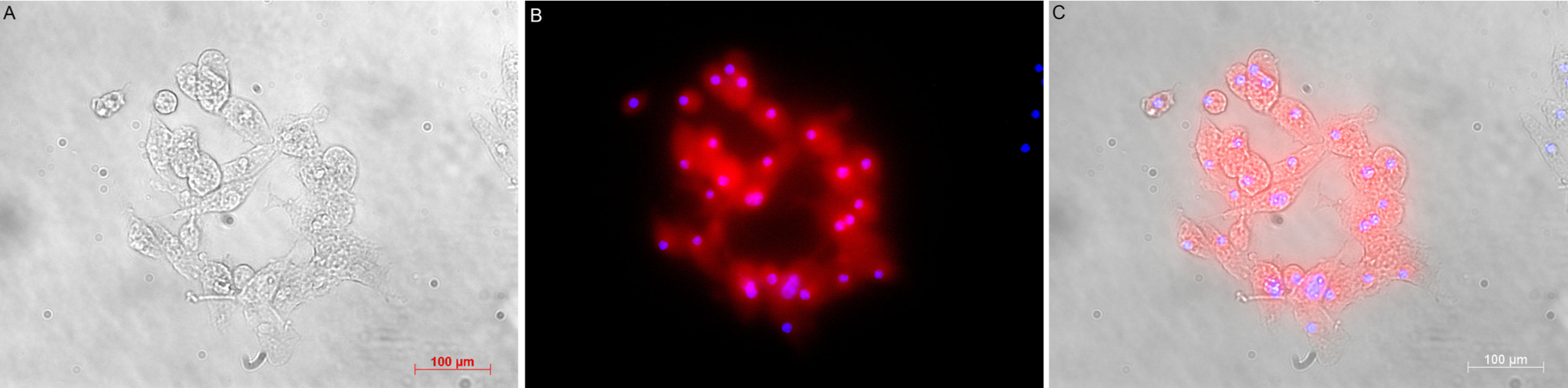
Methods: Whole brains were harvested from E13.5-14 Swiss mouse fetuses. Isolated cells were floating seeded to form spheroid bodies. Neurospheres were treated with one in fractions of ethanol 200-500 mg/mL, or nbutanol 200 mg/mL, or aqueous 200-500 mg/mL for 5 days. Neural stem cells could persistently generate secondary spheres. Neurospheres strongly expressed nestin, CD24 and deriving cells could differentiate into the GFAP-positive astrocyte-like cells.
Results: Ginseng fractions significantly promoted neurosphere growth rate. Particularly, 200 mg/mL ginseng ethanol fraction significantly increased the neurosphere size (28.00 +/- 3.00%, p<0.0001) not showing degeneration to the 5th day. However, n-butanol and aqueous fraction could not sustain the sphere structure. Ginseng ethanol fraction also elevated in the G2/M proportion (28.73+/-0.45%, p<0.0001), up-regulated proliferation mRNA ki67 (4.605+/-6.48 fold-change, p<0.05), cycA1 (12.61+/-4.65 fold-change, p<0.0001), cycD1 (22.47+/-8.18 fold-change, p<0.0001), cycC (9.53+/-2.63 fold-change, p<0.0001) compared with those of the n-butanol or aqueous fraction-treated neurospheres. Shorten G0/G1 phase (47.08 +/-0.16, p<0.0001), up-regulation of sox2 (71.25+/-27.24 fold-change, p<0.0001) mRNA levels indicated self-renewal effect of the ginseng ethanol fraction; however, those of n-butanol and aqueous fraction-treated neurospheres suggested an inhibiting effect on the cell proliferation.
Conclusion: Panax vietnamensis extract fractions had a positive effect on the proliferation of cultured neural stem cells. The ethanol fraction at 200 mg/mL could significantly promote the growth rate while still sustained the integrity of treated spheres.
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright The Author(s) 2017. This article is published with open access by BioMedPress. This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC-BY 4.0) which permits any use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author(s) and the source are credited.
