Study of the Association between Plasminogen Activator Inhibitor-1, other Inflammatory Markers, Metabolic Control Parameters, and Diabetic Foot Disease
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15419/bmrat.v9i3.733Keywords:
diabetic foot disease, PAI-1, type 2 diabetesAbstract
Background: The incidence of type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) has been increasing in recent years. As such, early identification and management of its complications—especially diabetic foot disease (DFD)—is of great importance. Multiple factors are involved in the pathogenesis of DFD; in this study, we aimed to study the association between plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 (PAI-1), high-sensitivity C-reactive protein (hs-CRP), 1st hour erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR), and DFD.
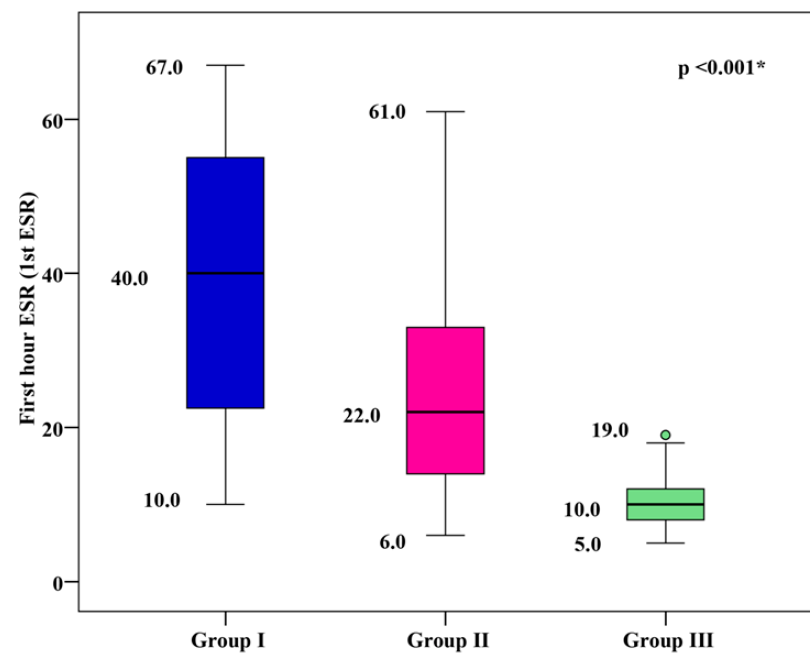
Methods: The present work was conducted on 200 T2DM patients with DFD (group I), 200 T2DM patients without DFD (group II), and 100 healthy subjects (group III, as a control group). Serum PAI-1 levels (using ELISA) and other inflammatory markers (hs-CRP and 1st hour ESR) were measured in the three groups.
Results: T2DM patients with DFD had significantly higher mean serum levels of inflammatory markers (including PAI-1, hs-CRP, and 1st hour ESR) compared to T2DM patients without DFD and the control group (p < 0.001). There was a significant positive correlation between inflammatory markers (including PAI-1, hs-CRP, and 1st hour ESR), metabolic control parameters (including fasting plasma glucose, 2-hour postprandial plasma glucose, and glycated hemoglobin), and severity of DFD in group I and group II (p < 0.001).
Conclusion: DFD is associated with elevated indicators of systemic and vascular inflammation. PAI-1, hs-CRP, and 1st hour ESR can be considered as early predictors for vascular tissue damage and can be used for early detection of complications in diabetic patients. Among these indicators, hs-CRP has greater diagnostic value in the detection of DFD.
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright The Author(s) 2017. This article is published with open access by BioMedPress. This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC-BY 4.0) which permits any use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author(s) and the source are credited.
