Green Synthesis of RES-CMCS: A Promising Modulator of the GLUT-4/Leptin Signaling Pathway in HFD-induced Insulin Resistance
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15419/bmrat.v9i7.753Keywords:
Resveratrol, RES-CMCS, insulin, total cholesterol, leptin, GLUT-4, rats and histopathologyAbstract
Introduction: Resveratrol (RES) is a multi-biofunctional compound found in grapes and mulberries. The present investigation was aimed at the green synthesis of resveratrol-carboxymethyl nanoparticles using low viscosity chitosan (RES-CMCS) and evaluation of their antidiabetic and antiobesity activity.
Methods: The obtained RES-CMCS was analyzed via measurement of zeta potential, particle size, morphology, and entrapment effectiveness. Its antidiabetic and antiobesity activities were also examined in an obese rat model.
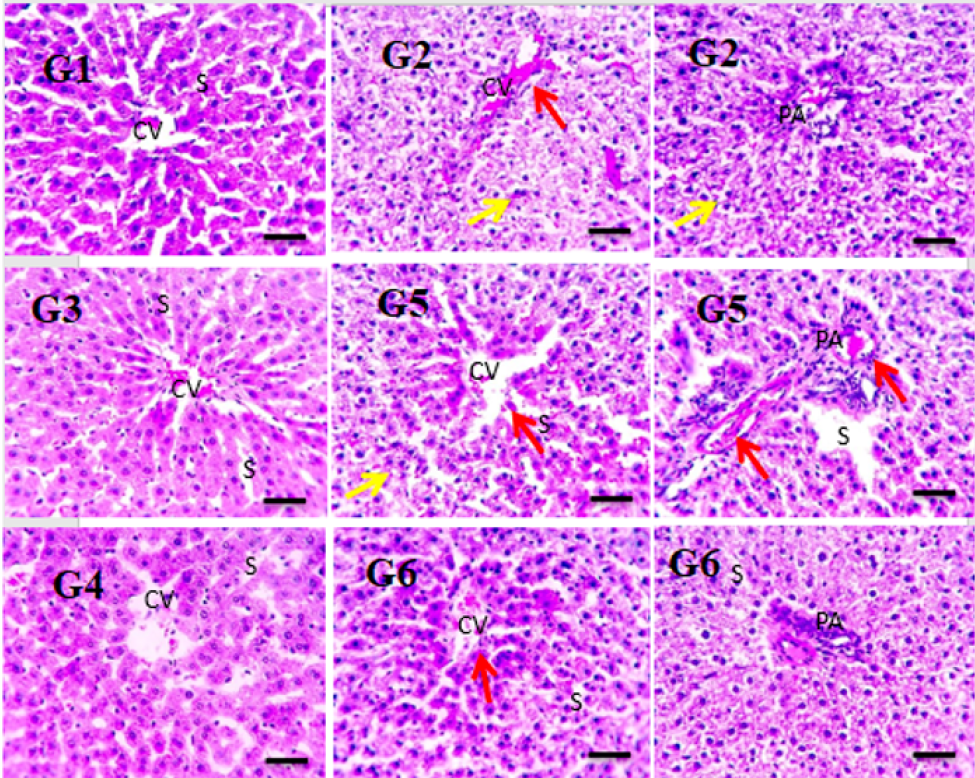
Results: The mean size of the RES-CMCS nanoparticles was 54.7 nm, the zeta potential was (-) 59.4 mV, and the entrapment effectiveness was 85.46%, with spherical nanoparticle morphology detected. In addition, treatment of obese diabetic rats with RES-CMCS (25 and 50 mg) as well as metformin (500 mg/kg.b.w) resulted in the normalization of several physiological parameters including body weight, levels of blood glucose, lipid profile, oxidative stress indicators, and expression of GLUT-4 and leptin genes.
Conclusions: The findings show the potential for RES-CMCS as a new pharmaceutical medication method for the treatment of obesity via modulation of antioxidant enzymes and expression of GLUT-4 and leptin.
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright The Author(s) 2017. This article is published with open access by BioMedPress. This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC-BY 4.0) which permits any use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author(s) and the source are credited.
