Analgesic, anti-inflammatory and hypouricemic effects of GT1 film-coated tablets on experimental animals
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15419/bmrat.v7i5.603Keywords:
GT1, pain relief, anti-inflammatory, hypouricemicAbstract
Aim: To evaluate pain relief, anti-inflammatory and hypouricemic effects of GT1 tablets on experimental animals.
Method: GT1 at the doses of 22.32 g/kg/day and 66.96 g/kg/day were evaluated for its analgesic effect in three models (hot plate, pain threshold, and acetic acid-induced writhing), its chronic anti-inflammatory effect in the granulomatous reaction model, and its hypouricemic effect in potassium oxonate-induced hyperuricemic mice. Acute anti-inflammatory effects of GT1 at the doses of 11.16 g/kg/day and 33.48 g/kg/day were evaluated in rats with two models: carrageenin-induced paw edema and peritonitis.
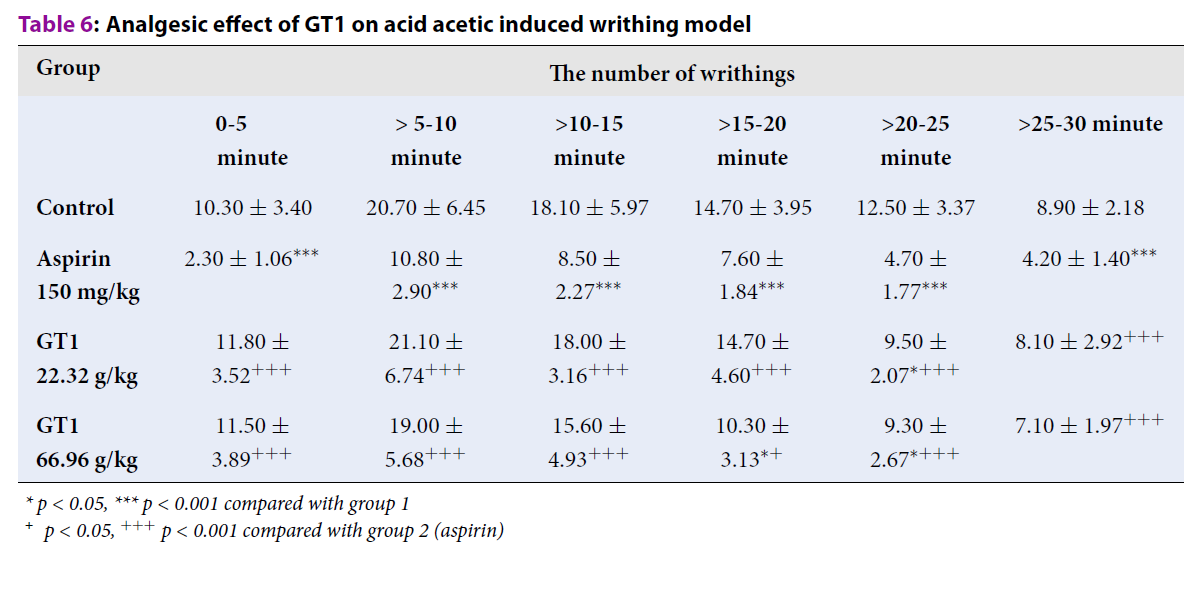
Results: GT1 prolonged the temperature reaction time on the hot plate (22.73 s and 20.37 s at both doses of 22.32 g/kg and 66.96 g/kg, respectively, compared to 16.96 s in control group), reduced the number of acid acetic-induced writhing effects, decreased the weight of granulomas, and decreased the level of acid uric in blood and urine (p < 0.05). GT1 caused a significant reduction in paw edema after subplantar injection of carrageenan in rats (p < 0.05). Moreover, there was a substantial decline of GT1 at the dose of 11.16 g/kg/day in terms of the volume and the quantity of protein in the inflammation fluid of the peritonitis model (p < 0.05).
Conclusion: GT1 at both doses of 11.16 g/kg/day and 33.48 g/kg/day posed acute anti-inflammatory effects on rats. GT1 at both doses of 22.32 g/kg/day and 66.96 g/kg/day exerted analgesic, chronic anti-inflammatory and hypouricemic effects on mice.
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright The Author(s) 2017. This article is published with open access by BioMedPress. This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC-BY 4.0) which permits any use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author(s) and the source are credited.
