Antioxidant effects of hydro-alcoholic extract of Ashrasi date palm in hepatotoxicity caused by mercuric chloride administration
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15419/bmrat.v7i6.613Keywords:
Antioxidant, Ashrasi Date palm, Mercuric chloride, HepatotoxicityAbstract
Introduction: date palm (ADP) is a flowering plant type of the palm family which has strong antioxidant properties. Mercuric chloride (MC) is a complex substance that generates oxidative stress. This study was designed to investigate the protective effects of ADP on the , inflammatory, oxidative and apoptotic changes induced by MC.
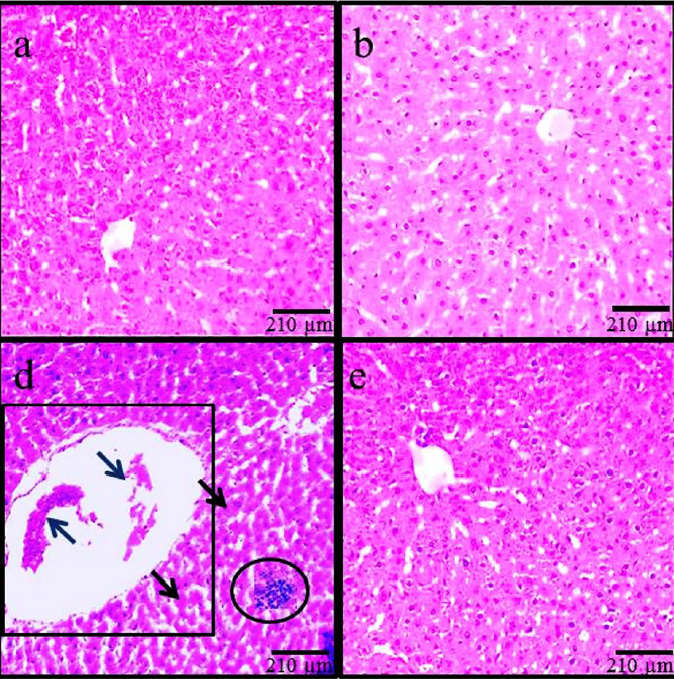
Methods: Fifty-six male rats were randomly allocated into 8 groups (n = 7) as follows: Group 1- control, 2- MC (50 mg/kg), 3-5: ADP (30, 90, and 270 mg/kg), and 6-8: MC+ADP. The rats were orally and administrated with the respective agents for 5 weeks. Extracts of ADP were prepared and screening was conducted. Nitric oxide (NO), lipid (LP), and Ferric Reducing Ability of Plasma (FRAP) assays were conducted to assess the antioxidant index. The levels of p53, Bcl2 and Bax gene expression were assessed by real-time PCR. Cytokines involved in inflammation were evaluated by enzyme-linked assay (ELISA). Liver enzymes were also measured using biochemical methods. changes (e.g. in hepatocyte (HD) and central hepatic vein (CHV)), and apoptosis cell index were evaluated by light and fluorescent microscopy methods.
Results: MC treatment significantly increased all parameters described in the Methods section (except for FRAP level and Bcl2 expression level, which were both decreased) in the MC group, when compared to the control group (P < 0.05). Also, all indices were significantly decreased in the ADP and ADP+MC groups (except for FRAP level and Bcl2 expression level, which were increased), when compared to the MC group (P < 0.05).
Conclusion: These findings revealed that ADP extract can serve as a potent antioxidant which effectively attenuates the adverse effects of MC on the liver through the activation of antioxidant mechanisms and regeneration of modifications.
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright The Author(s) 2017. This article is published with open access by BioMedPress. This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC-BY 4.0) which permits any use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author(s) and the source are credited.
