A preliminary study on the association between pro-inflammatory cytokine IL-1 beta polymorphisms and susceptibility to hepatitis C infection in Malay male Malay drug abusers
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15419/bmrat.v10i2.794Keywords:
hepatitis C, interleukin-1b (IL-1b ), polymerase chain reaction-restriction fragment length polymorphism (PCR-RFLP), Malay male, single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP)Abstract
Introduction: Hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection frequently leads to liver complications, such as fibrosis, cirrhosis, and hepatocellular carcinoma. The incidence of HCV infection transmission among drug abusers is concerning. Interleukin-1 beta (IL-1b) is a pro-inflammatory cytokine secreted during innate and adaptive immune responses and plays a pivotal role in chronic inflammatory diseases. Functional single nucleotide polymorphisms in IL-1b cause it to play different roles in disease susceptibility and progression. This study aimed to investigate the association between genetic polymorphisms of pro-inflammatory cytokines (IL-1b) and HCV infection susceptibility in Malay male drug abusers.
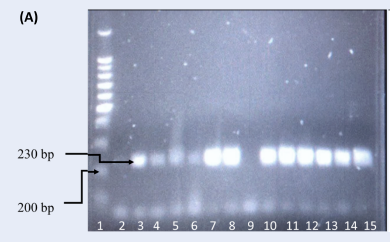
Methods: In total, 48 male Malay drug abusers were included in this retrospective case-control study. Genomic DNA was extracted from whole blood samples and analyzed using polymerase chain reaction-restriction fragment length polymorphism (PCR-RFLP) for the IL-1b rs16944 and rs1143634 polymorphisms.
Results: Analysis of IL-1b rs1143634 revealed that the C/C genotype was common in both the case and control groups; however, no statistical significance was observed (p = 0.068, c2 = 3.755). Genotyping of IL-1b demonstrated that all samples were of the homozygous mutant type (T/T).
Conclusion: There was no association between IL-1b polymorphism (rs1143634 and rs16944) and hepatitis C infection susceptibility among Malay male drug abusers.
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright The Author(s) 2017. This article is published with open access by BioMedPress. This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC-BY 4.0) which permits any use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author(s) and the source are credited.
