Statin-associated new-onset diabetes mellitus and insulin resistance: a 30-year bibliometric study (1992- 2022)
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15419/bmrat.v10i11.845Keywords:
Statin, New-onset diabetes mellitus, Insulin resistance, Bibliometric analysis, Web of scienceAbstract
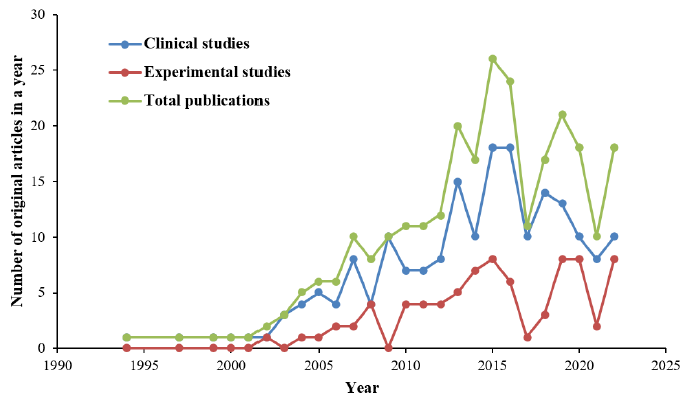
Statins are widely used lipid-lowering drugs that are relatively well-tolerated and have an established safety profile. However, statin therapy has been reported to increase the risk of developing new-onset type 2 diabetes mellitus (NOD2). Although this side effect is rare, research on this topic is still ongoing. This bibliometric study was performed to provide an overview of the dynamics of research on statin-associated NOD2 and insulin resistance from the initial report to the year 2022. Original articles related to statin-associated NOD2 and insulin resistance were selected and retrieved from the Web of Science database. A quantitative analysis of publication trends, the contributions of different countries and funding agencies, and the most highly cited articles were then tabulated. The citation networks and the co-occurrence analysis of keywords of the included articles were illustrated with VOSviewer. A total of 271 research articles were included and analysed. The years 2012 to 2016 were prolific in research on statin-associated NOD2 and insulin resistance, followed by a decreasing trend in publications on this topic in many countries, particularly from 2020 to 2021. However, researchers from South Korea and China seem to have had a continued interest in this research area and the trend in publications increased again in 2022. Based on this trend, it is predicted that the number of pertinent articles in the coming years will be maintained or will continue to rise. The co-occurrence analysis of keywords showed that ``atorvastatin'' occurred more often than other statins. Among the thematic areas of research on statin-associated NOD2 and insulin resistance that were identified in this study were ``heterogeneity'', ``peripheral glucose uptake and insulin sensitivity'', ``tissue inflammation and oxidative stress'' and ``targeted tissues''. This is the first bibliometric study to predict the trends and provide an overview of the progress of research on statin-associated NOD2 and insulin resistance.
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright The Author(s) 2017. This article is published with open access by BioMedPress. This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC-BY 4.0) which permits any use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author(s) and the source are credited.
